Quality management plays a crucial role in the success of small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). By implementing effective quality management practices, SMBs can transform their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive overall growth. In this article, we will explore the key must-haves for quality management in SMBs and how these practices can lead to business excellence.
Quality management is not limited to large organizations; it is equally important for SMBs. Implementing quality management practices helps SMBs streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. By focusing on quality, SMBs can build a strong reputation, increase customer loyalty, and drive sustainable growth.
Effective quality management practices also enable SMBs to identify and address potential risks, minimize errors and defects, and optimize resource allocation. This results in cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced competitiveness in the market. Quality management is not just about meeting regulatory requirements; it is about creating a culture of excellence that permeates every aspect of the organization.
When selecting quality management practices for SMBs, several key criteria should be considered. These criteria ensure that the chosen practices align with the unique needs and goals of the organization. The following are some essential selection criteria for quality management practices in SMBs:
Efficient and effective processes are the backbone of quality management. SMBs should focus on implementing practices that streamline their internal processes, eliminate waste, and optimize resource utilization. This includes process mapping, automation, and continuous improvement methodologies such as Lean Six Sigma.
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is vital for SMBs to maintain the quality of their products and services. Implementing quality management practices that align with recognized standards, such as ISO 9001, ensures that SMBs meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Customer satisfaction is a fundamental aspect of quality management. SMBs should prioritize practices that enable them to gather customer feedback, measure satisfaction levels, and implement improvements based on customer insights. This includes implementing customer feedback systems, conducting surveys, and monitoring online reviews.
Engaged and well-trained employees are essential for achieving and maintaining high-quality standards. SMBs should invest in training programs that equip their employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver quality products and services. Employee engagement initiatives, such as recognition programs and regular communication, also contribute to a culture of quality.
Continuous improvement is at the heart of quality management. SMBs should adopt practices that foster a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to identify and implement innovative ideas and solutions. This includes methodologies like Kaizen and the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle.
Now that we have discussed the key selection criteria for quality management practices, let’s dive into a comprehensive review of the 15 quality management must-haves for SMBs.
Continuous improvement methodologies provide SMBs with structured approaches to enhance their processes and drive innovation. These methodologies focus on eliminating waste, reducing variation, and continuously optimizing operations. Some popular continuous improvement methodologies include Lean Six Sigma, Kaizen, and the PDCA cycle.
Eager to streamline your processes and drive innovation? Contact us for a free quote and see how continuous improvement methodologies can elevate your business.
Gathering and analyzing customer feedback is crucial for SMBs to understand customer needs, preferences, and pain points. Customer feedback systems provide a structured approach to collecting, analyzing, and acting on customer feedback. This helps SMBs identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance customer satisfaction.
Discover how customer feedback can transform your business. Get in touch for a free quote and start enhancing customer satisfaction today!
Compliance with quality standards is essential for SMBs to demonstrate their commitment to quality and gain a competitive edge. ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized quality management standard that provides a framework for implementing effective quality management systems. Achieving ISO 9001 certification signals to customers that an SMB follows best practices and consistently delivers high-quality products and services.
Ready to boost your credibility in the marketplace? Reach out for a free quote on ISO 9001 compliance and take your quality standards to the next level.


Effective risk management is crucial for SMBs to identify and mitigate potential risks that could impact product quality or customer satisfaction. Implementing risk management strategies allows SMBs to proactively address risks, minimize their impact, and ensure business continuity. This includes conducting risk assessments, developing contingency plans, and regularly monitoring and evaluating risks.
Minimize risks and protect your operations. Contact us for a free quote on implementing effective risk management strategies.

Investing in quality training programs equips SMB employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver high-quality products and services. These programs provide employees with a clear understanding of quality standards, processes, and best practices. Quality training programs can cover a range of topics, including quality control, process improvement, and customer service.
Invest in your team’s growth with our quality training programs. Get a free quote today and start fostering a culture of excellence.

Data analysis tools play a crucial role in quality management by providing insights into product quality, process performance, and customer satisfaction. These tools help SMBs collect, analyze, and interpret data to identify trends, anomalies, and areas for improvement. Data analysis tools can range from simple spreadsheet software to advanced statistical analysis tools.
Turn data into actionable insights for quality improvement. Contact us for a free quote on advanced data analysis tools.
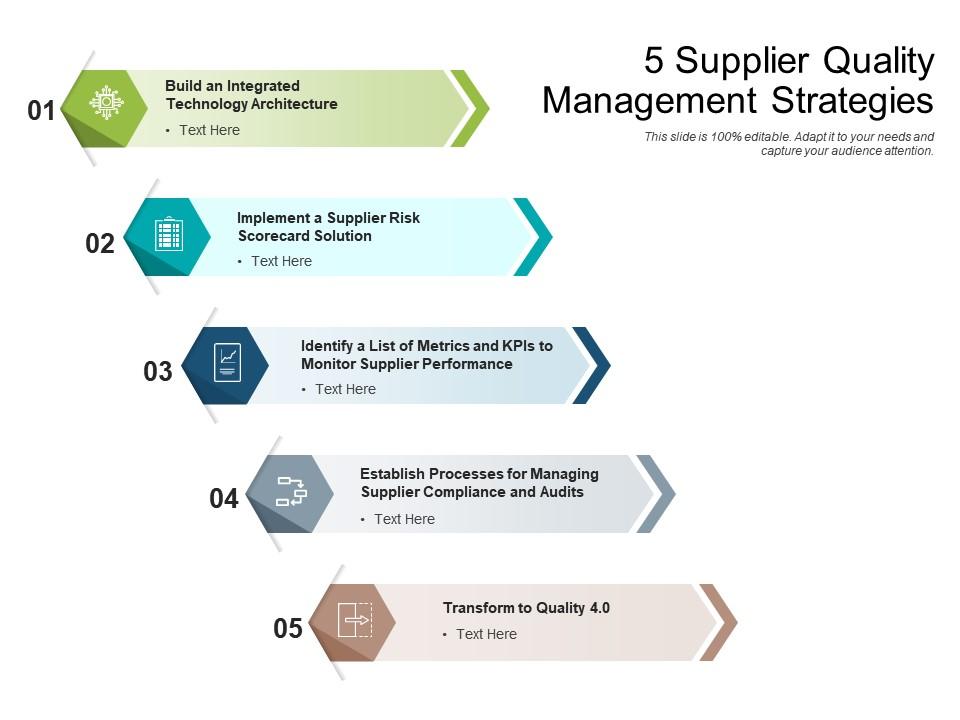
Supplier quality management is essential for SMBs to ensure that the materials and services they receive meet the required standards. Implementing supplier quality management techniques enables SMBs to assess and monitor their suppliers’ performance, ensure product consistency, and minimize the risk of defects or non-compliance. This includes conducting supplier audits, establishing quality agreements, and implementing supplier performance measurement systems.
Ensure the quality of your supply chain. Get a free quote on our supplier quality management techniques today.
Documenting and standardizing processes is essential for SMBs to ensure consistency, reduce errors, and facilitate continuous improvement. Process documentation provides a clear understanding of how tasks and activities are performed, enabling employees to follow standardized procedures. This includes creating process flowcharts, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and work instructions.
Streamline your operations with effective process documentation. Reach out for a free quote and start standardizing your processes.
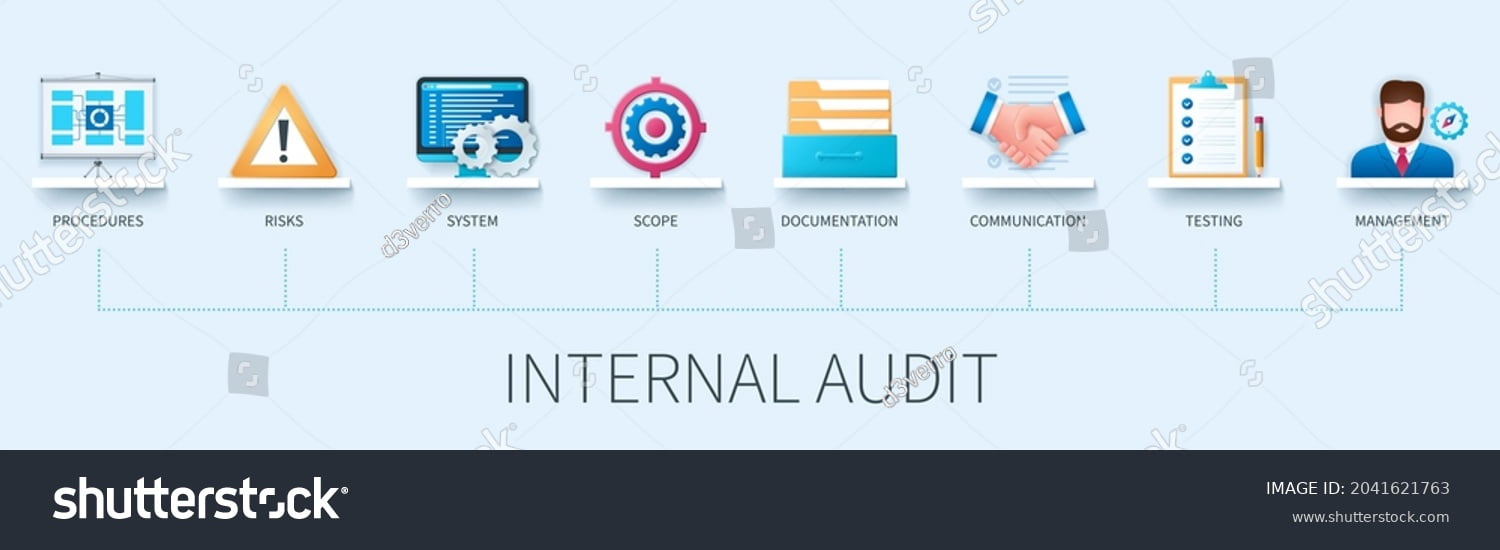
Internal audits play a crucial role in quality management by providing an independent assessment of an organization’s processes, systems, and controls. Implementing internal audit systems helps SMBs identify areas for improvement, ensure compliance with standards, and drive continuous improvement. Both external auditors and trained employees are capable of conducting internal audits.
Enhance your quality management with our internal audit systems. Contact us for a free quote and take the first step towards continuous improvement.
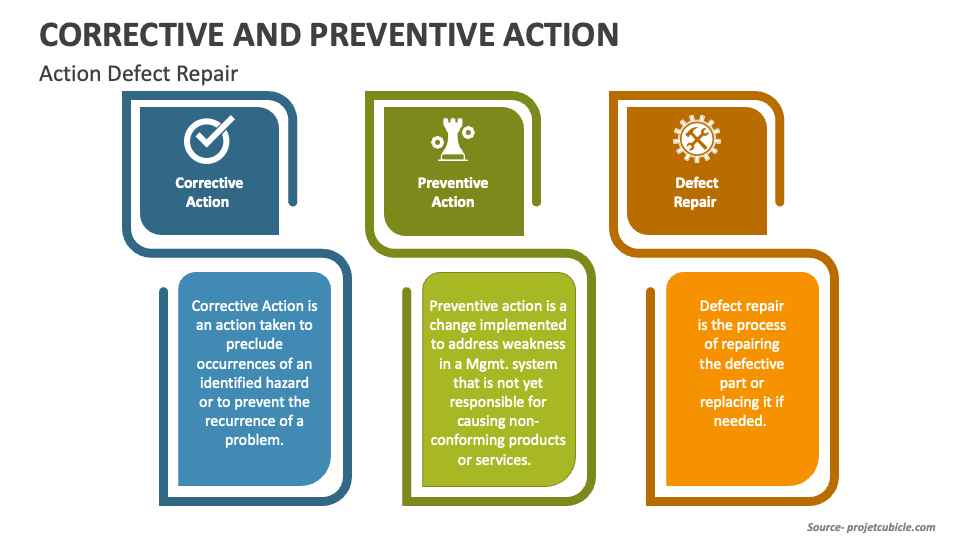
Corrective and preventive action (CAPA) plans are crucial for addressing non-conformities, preventing recurrence, and driving continuous improvement. CAPA plans provide a structured approach to identifying the root causes of quality issues, implementing corrective actions, and establishing preventive measures to avoid future problems. This includes root cause analysis, action plan development, and monitoring of effectiveness.
Address quality issues effectively with our CAPA plans. Get a free quote and prevent future non-conformities.
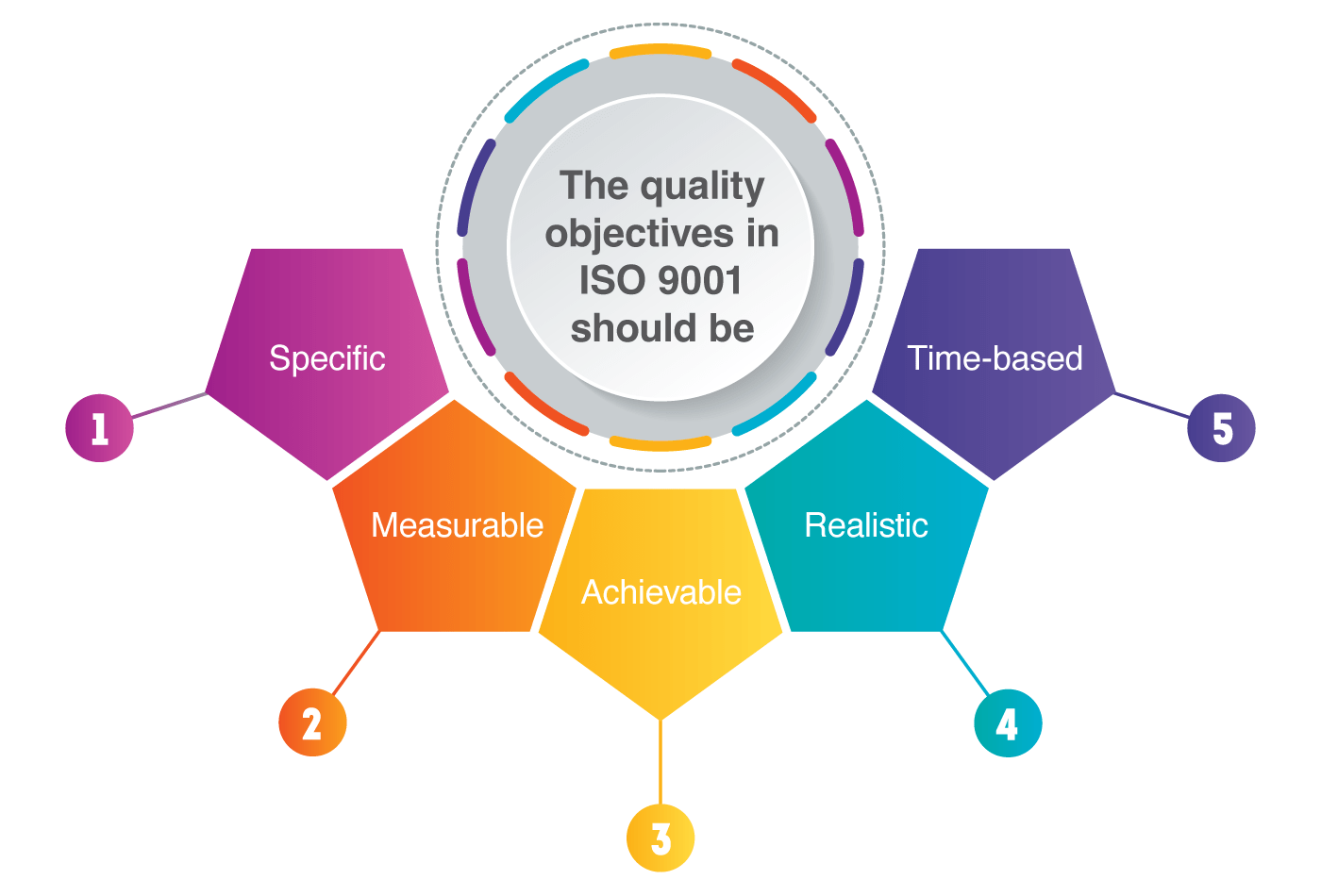
Setting quality objectives provides SMBs with a clear direction and focus for their quality management efforts. Quality objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By setting quality objectives, SMBs can align their quality management initiatives with their overall business goals and monitor progress towards achieving those objectives.
Set clear and achievable quality objectives with our expert guidance. Contact us for a free quote and align your goals with business success.
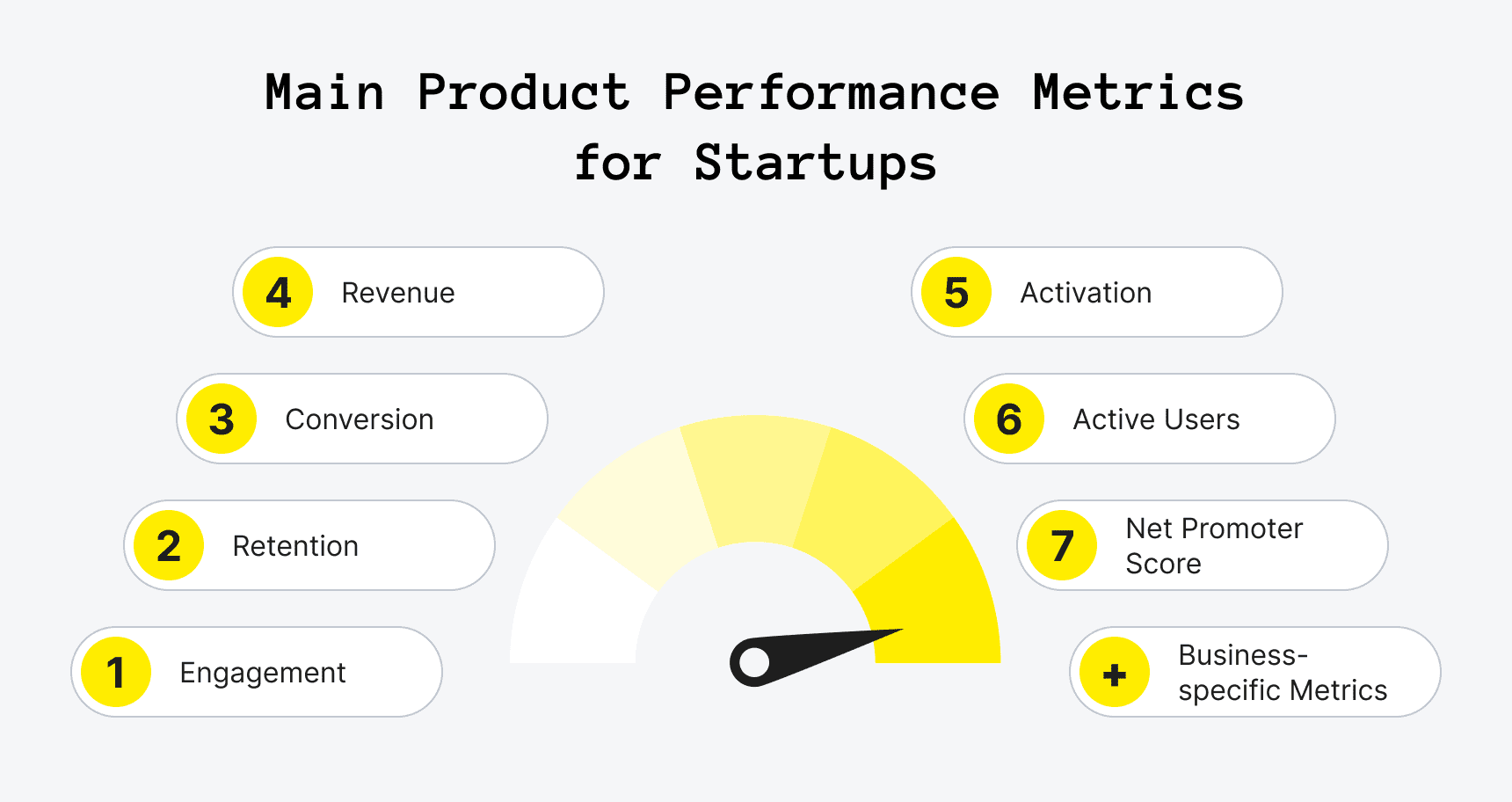
Performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for measuring and monitoring the effectiveness of quality management initiatives. These metrics provide SMBs with objective data to assess performance, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. Performance metrics and KPIs can include customer satisfaction scores, defect rates, on-time delivery performance, and employee engagement levels.
Measure what matters with our performance metrics and KPIs. Get a free quote and start tracking your quality progress.
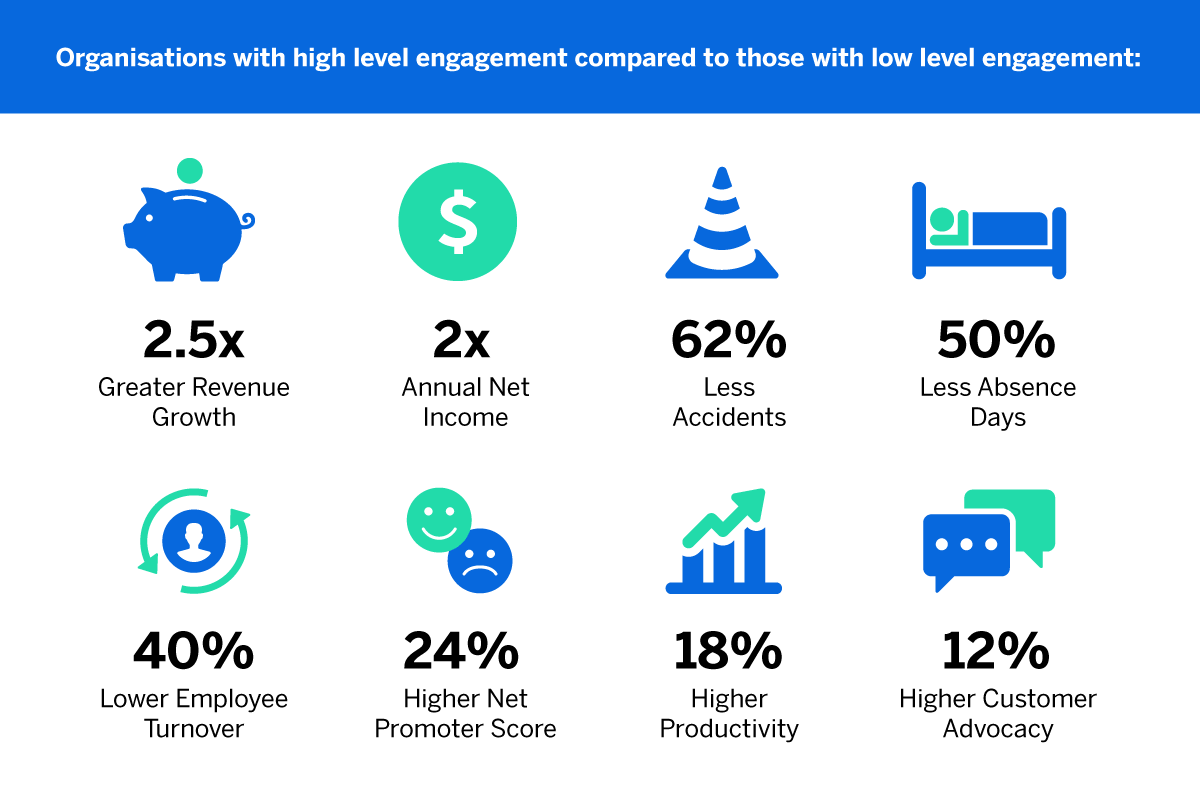
Employee engagement is a critical factor in the success of quality management initiatives. Engaged employees are more likely to embrace quality principles, contribute to continuous improvement, and deliver high-quality products and services. SMBs should implement strategies to foster employee engagement, including recognition programs, training opportunities, and open communication channels.
Boost employee engagement in quality initiatives. Contact us for a free quote and build a committed workforce.
Leveraging technology is essential for SMBs to streamline their quality management processes, gather and analyze data, and drive continuous improvement. Technology integration can range from simple software solutions to more advanced quality management systems. By adopting technology solutions, SMBs can automate manual processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance collaboration.
Leverage technology to enhance your quality management. Get a free quote on our tech solutions today.
Leadership and organizational culture play a crucial role in fostering a culture of quality within SMBs. Strong leadership sets the tone for quality management initiatives, defines expectations, and provides resources and support. An organizational culture that values quality promotes employee engagement, encourages innovation, and drives continuous improvement.
Foster a culture of quality with strong leadership. Reach out for a free quote and lead your business towards excellence.

Implementing quality management practices is essential for SMBs to thrive in today’s competitive market. By adopting the 15 must-haves discussed in this article, SMBs can transform their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth. Whether it’s continuous improvement methodologies, customer feedback systems, or technology integration, each must-have contributes to building a culture of quality and excellence. Contact us today to learn how these quality management must-haves can benefit your SMB and take your business to the next level.

