Antimalware service executable : 3 effective strategies to reduce CPU load
Introduction
The Antimalware Service Executable, also known as MsMpEng.exe, plays a crucial role in Windows Defender by protecting your system from malware and other security threats. However, many users have reported that this process can cause high CPU and memory utilization, leading to performance issues. In this article, we will explore effective strategies to reduce CPU load caused by the Antimalware Service Executable and optimize your system's performance.
Understanding the Antimalware service executable
The Antimalware Service Executable is a critical process within Windows Defender, responsible for scanning and protecting your system from malicious software. It constantly monitors your files, downloads, and programs, ensuring that your system remains secure. However, due to various reasons, this process can consume a significant amount of CPU resources, leading to performance degradation. Let's delve into some of the factors that contribute to its high CPU usage.
High CPU or Disk usage reasons
There are several reasons why the Antimalware Service Executable may consume a high amount of CPU or disk resources. These include:
- Real-Time protection: Windows Defender's real-time protection feature constantly scans files and processes in real-time, which can put a strain on your CPU.
- Scheduled scans: Windows Defender performs regular scheduled scans to ensure your system's security. These scans can impact CPU performance, especially if they occur during peak usage times.
- Excessive file activity: If you have a large number of files or folders, or if you frequently download or transfer files, the Antimalware Service Executable may consume more CPU resources to scan and protect these files.
Now that we understand the reasons behind the high CPU usage, let's explore some effective solutions to reduce the CPU load caused by the Antimalware Service Executable.
Solutions to resolve high CPU consumption by Antimalware service executable
Solution 1: Perform a clean boot
Performing a clean boot on your PC can help determine if a background program is causing the high CPU usage. Here's how you can do it:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Alternatively, you can go to Start and search for "Run". In the Run dialog box, type "msconfig" and hit enter.
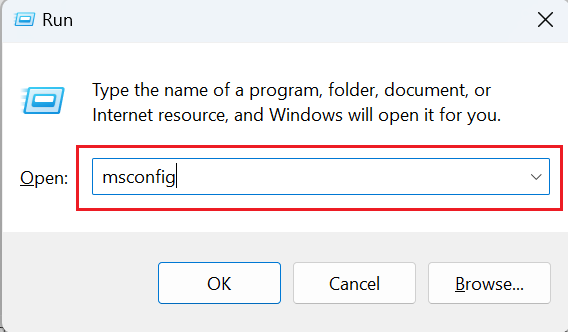
- This will open the System Configuration window.
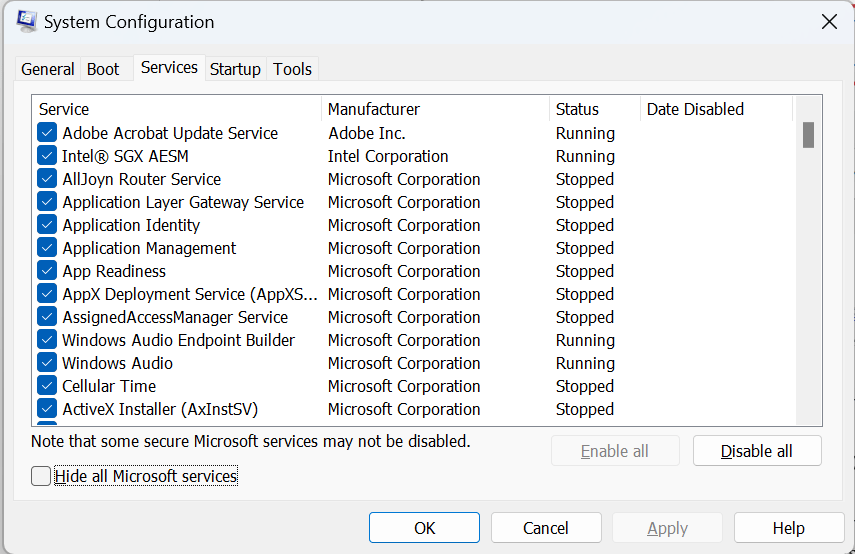
- Go to the "Services" tab and check the box that says "Hide all Microsoft services"

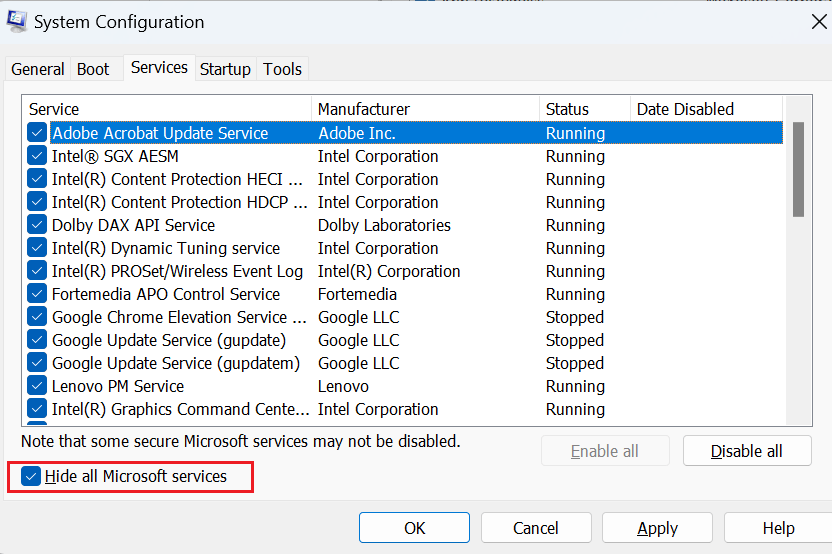
- Click on "Disable all" to disable all non-Microsoft services.

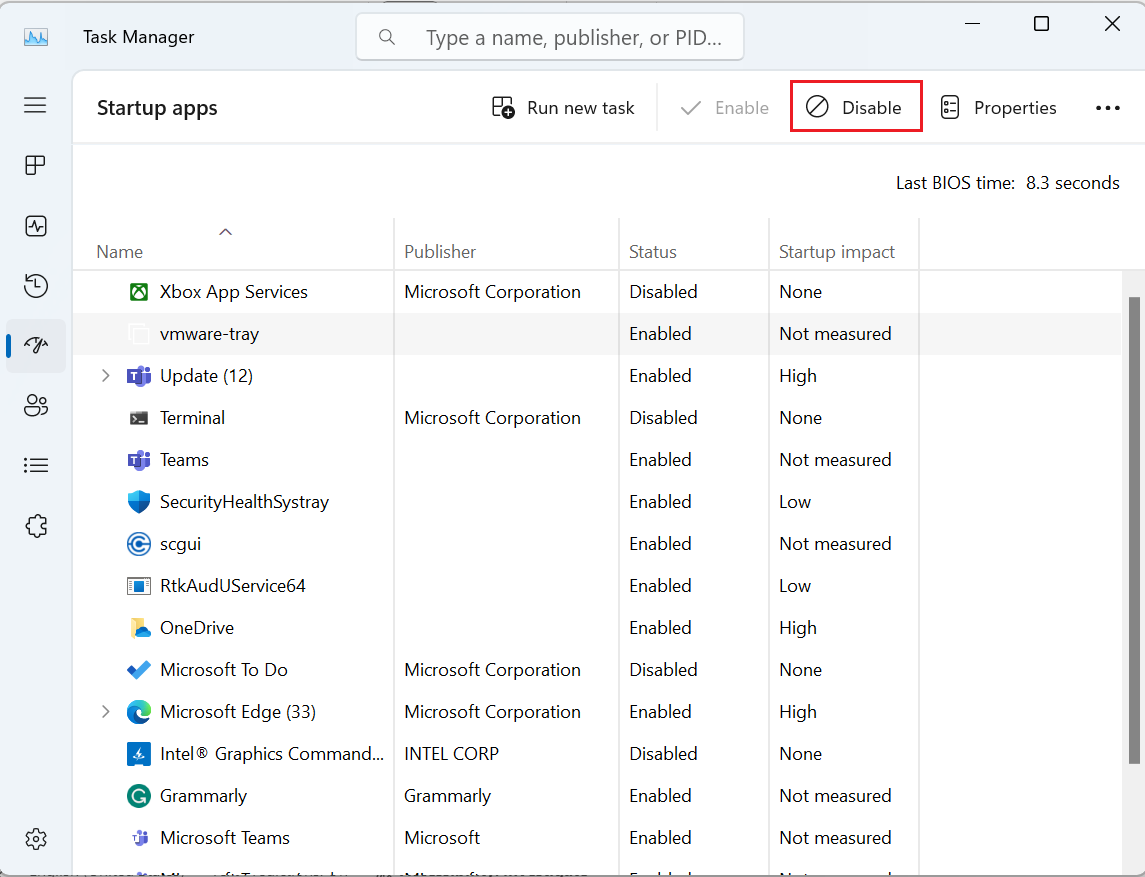
- Next, go to the "Startup" tab and click on "Open Task Manager."

- In the Task Manager, disable all the startup programs by right-clicking on each program and selecting "Disable."
- Close the Task Manager and go back to the System Configuration window. Click on "Apply" and then "OK."
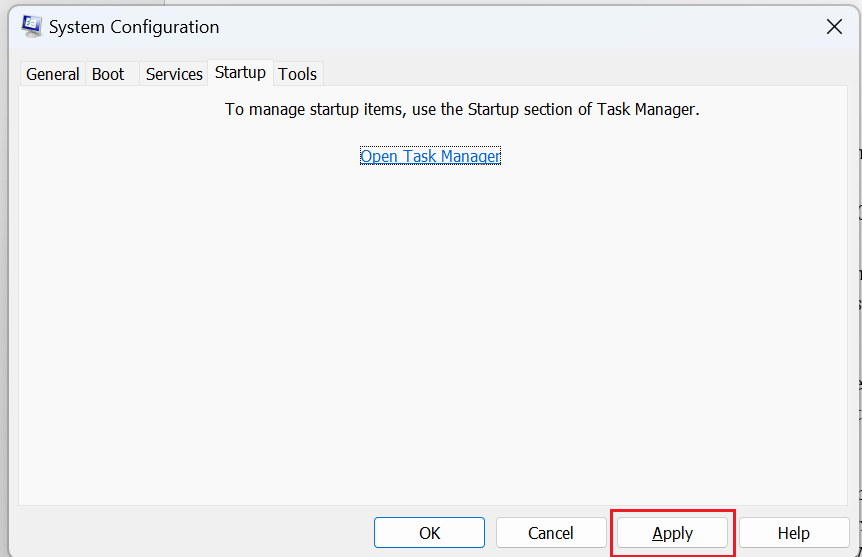
- Restart your computer and check if the CPU usage has improved. If it has, you can gradually enable the services and startup programs one by one to identify the culprit.
Solution 2: Adjust Windows defender's schedule
The Windows Defender scheduled scans can contribute to the high CPU usage. By adjusting the schedule, you can minimize the impact on your system's performance. Follow these steps:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
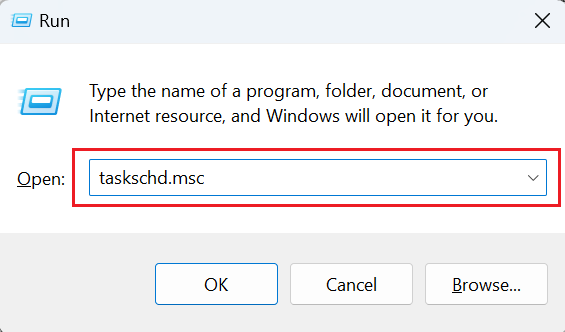
- Type "taskschd.msc" and hit enter. This will open the Task Scheduler.
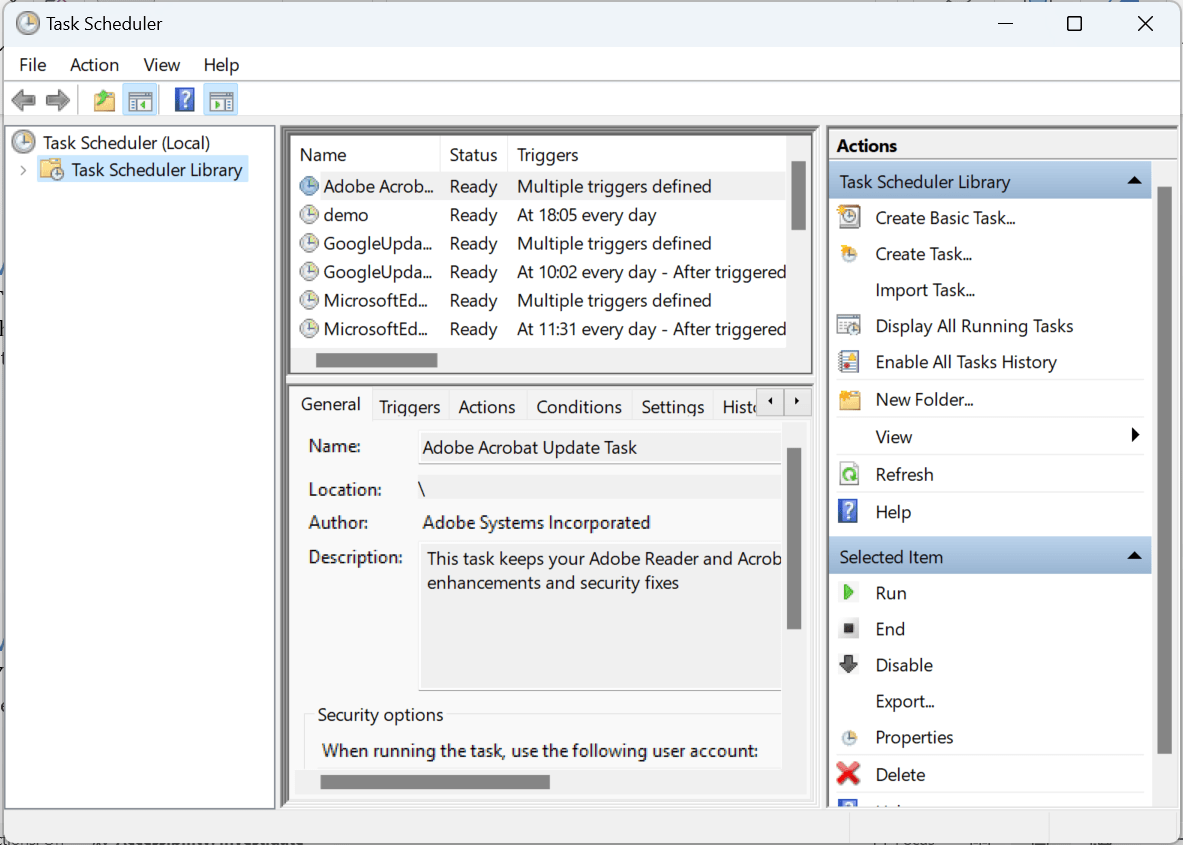
- Navigate to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.

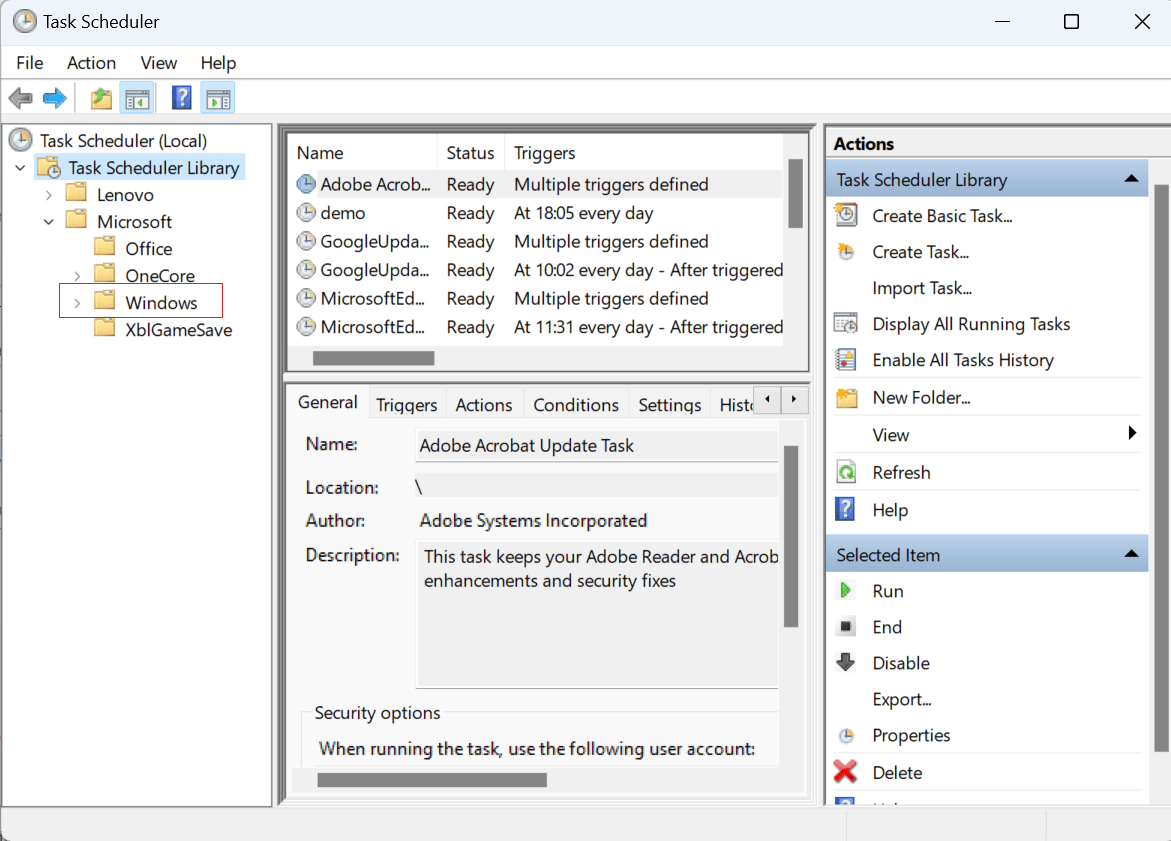
- Double-click on "Windows Defender Scheduled Scan" in the right-hand pane.

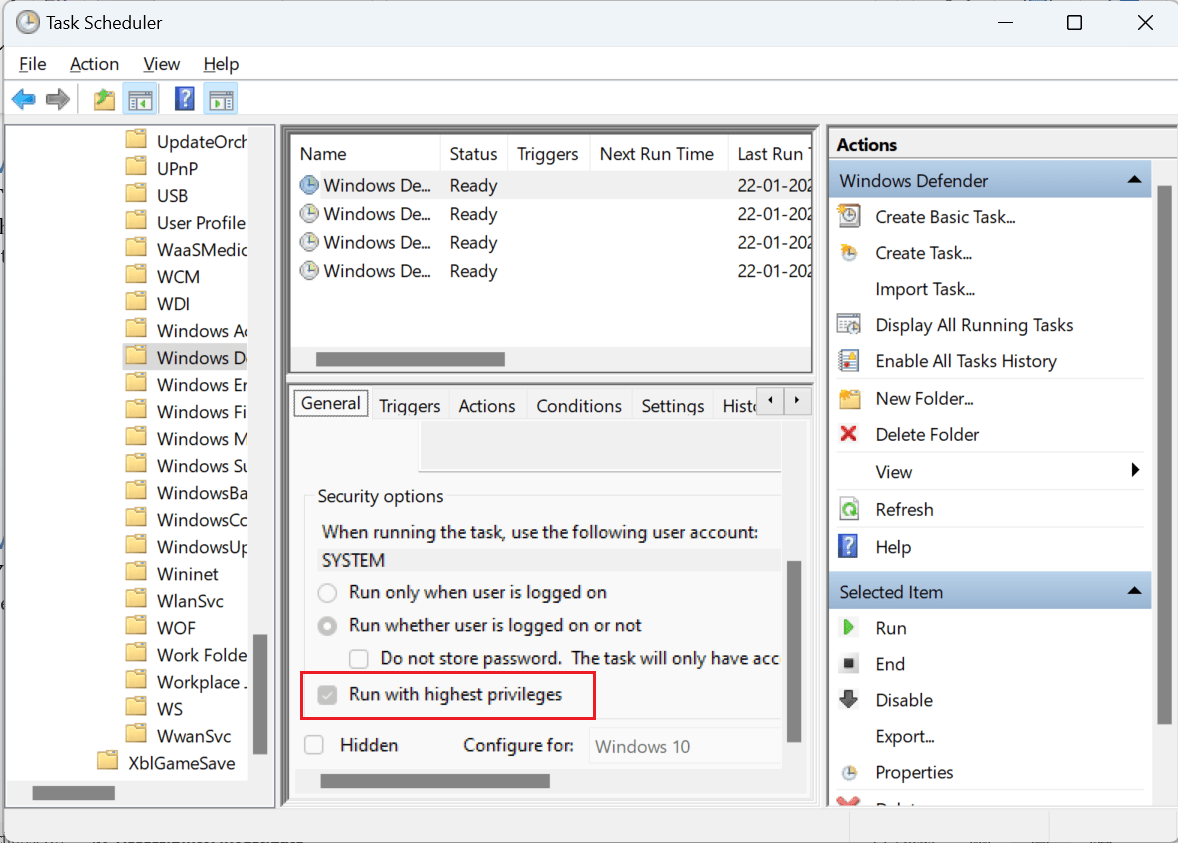
- In the General tab, uncheck the option that says "Run with highest privileges"
- Switch to the Conditions tab and uncheck all the options.
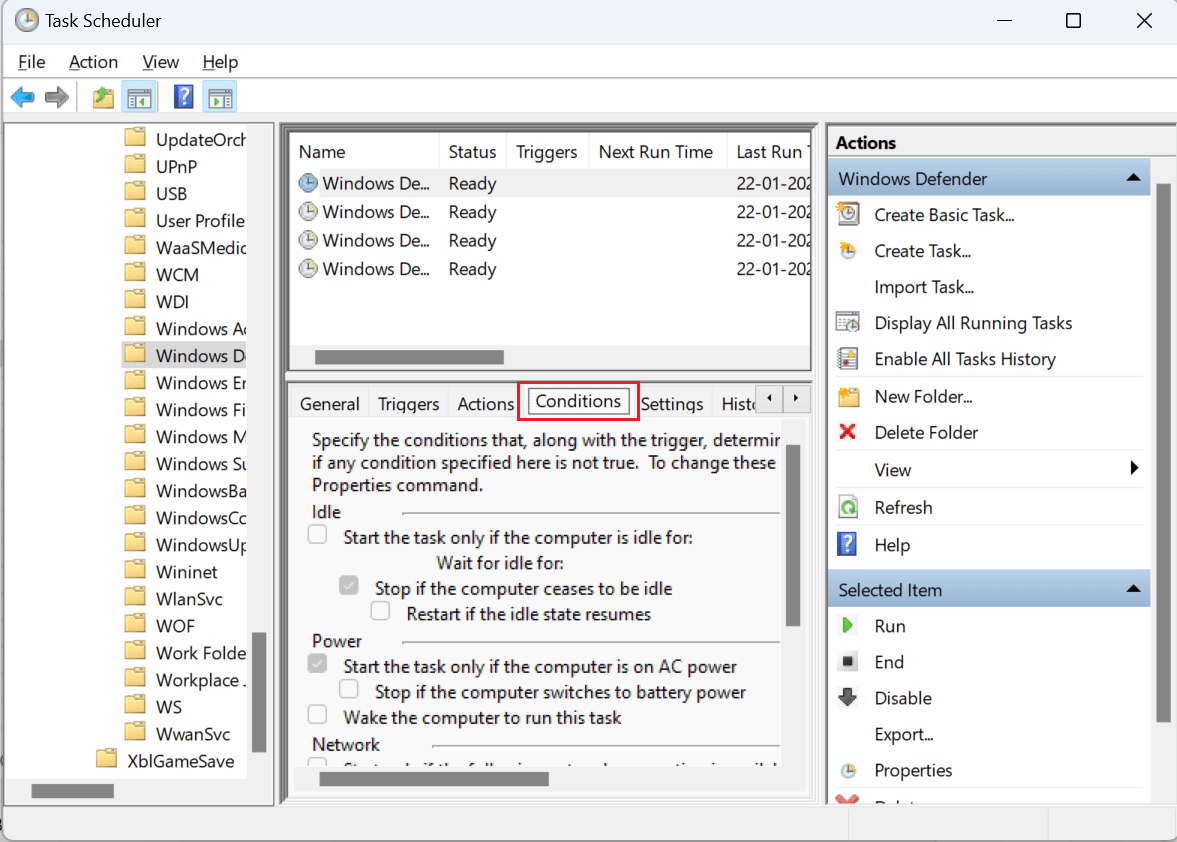
Click on "OK" to save the changes.
Solution 3: Exclude MsMpEng.exe from Windows defender scans
You can exclude the Antimalware Service Executable from Windows Defender scans to reduce its impact on CPU usage. Here's how:
- Open Windows Defender by searching for it in the Start menu.
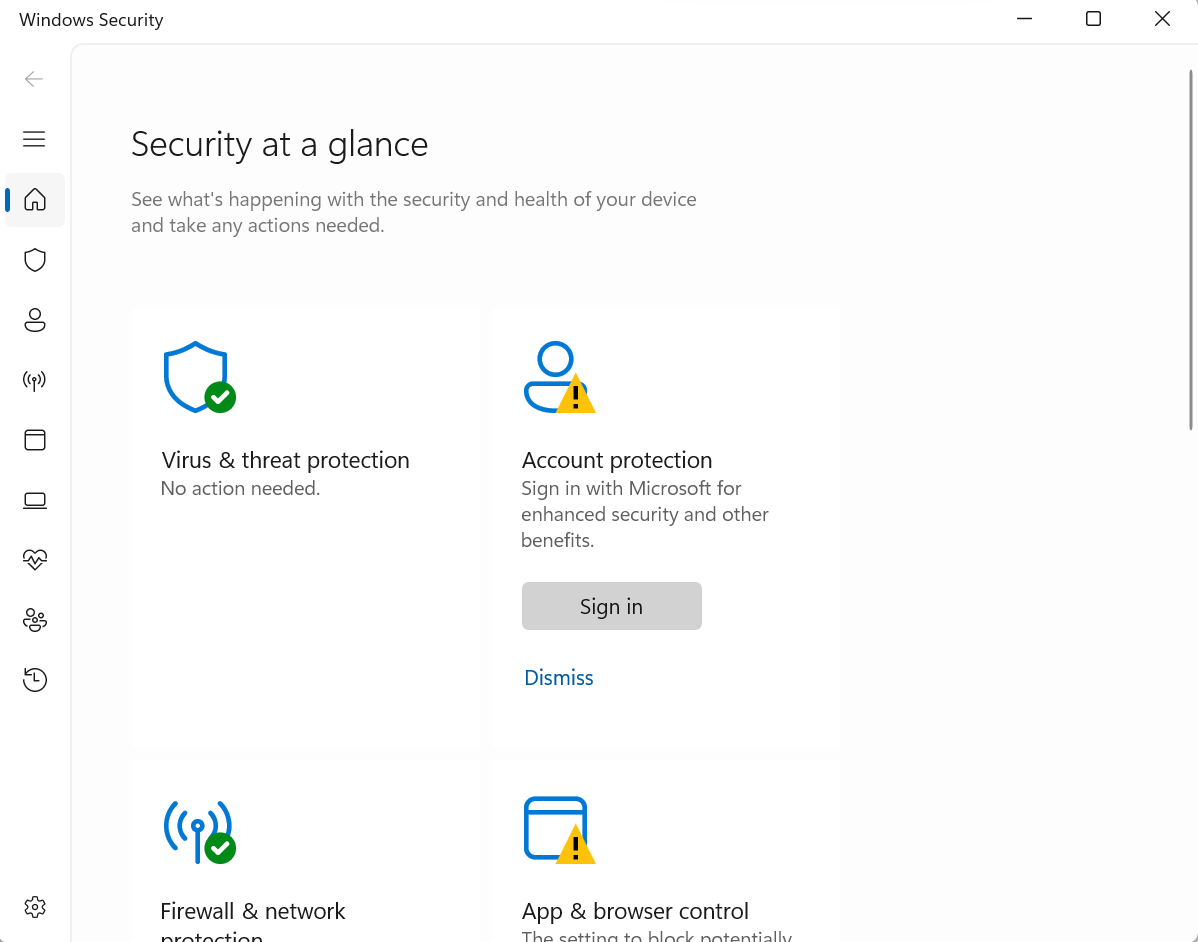
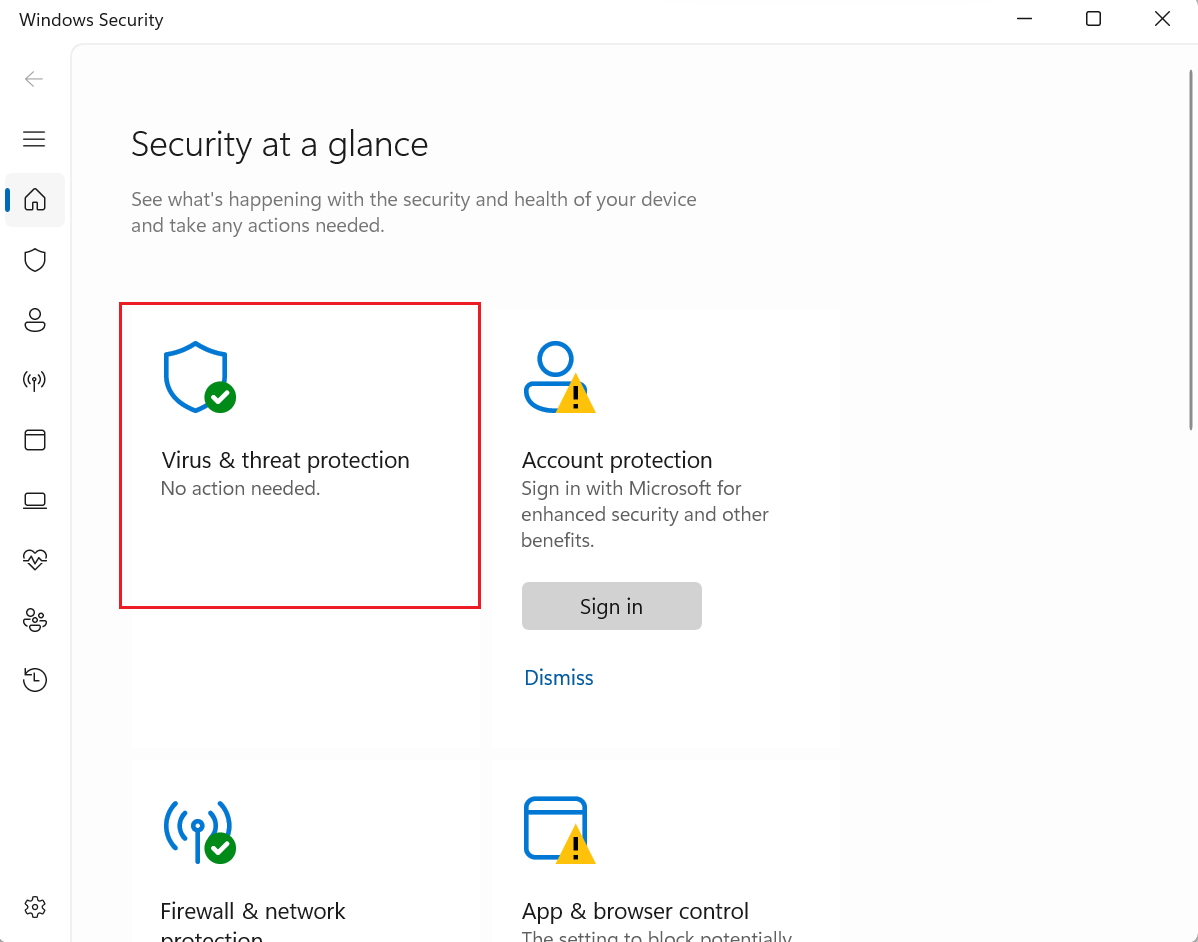
- Click on "Virus & threat protection" and then select "Virus & threat protection settings"
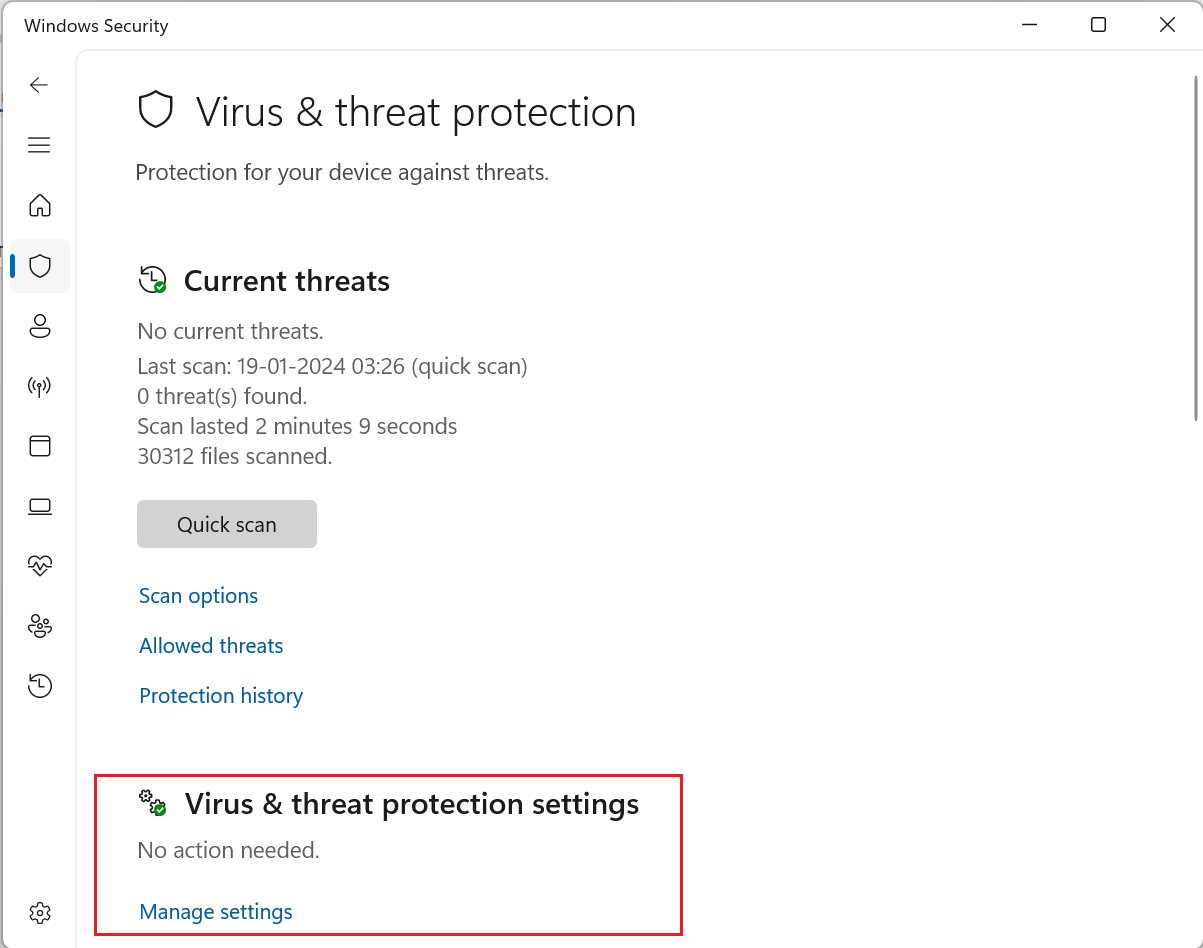
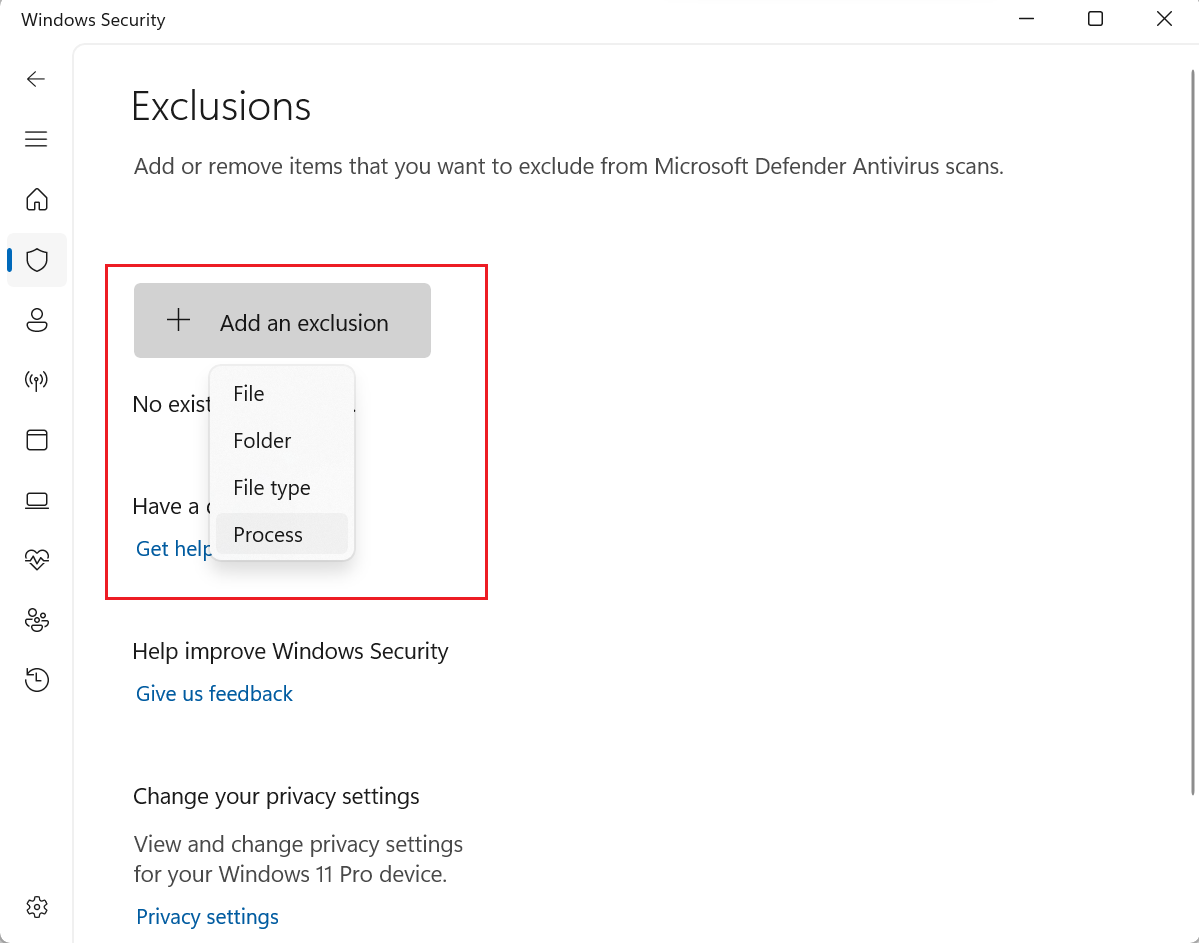
- Under the "Exclusions" section, click on "Add or remove exclusions"

- Choose "Process" from the dropdown menu.
- In the "Add an exclusion" window, type "MsMpEng.exe" and click on "Add"
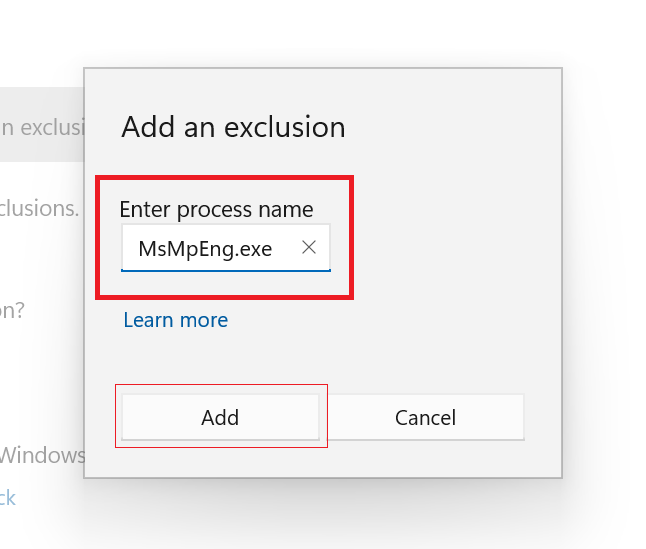
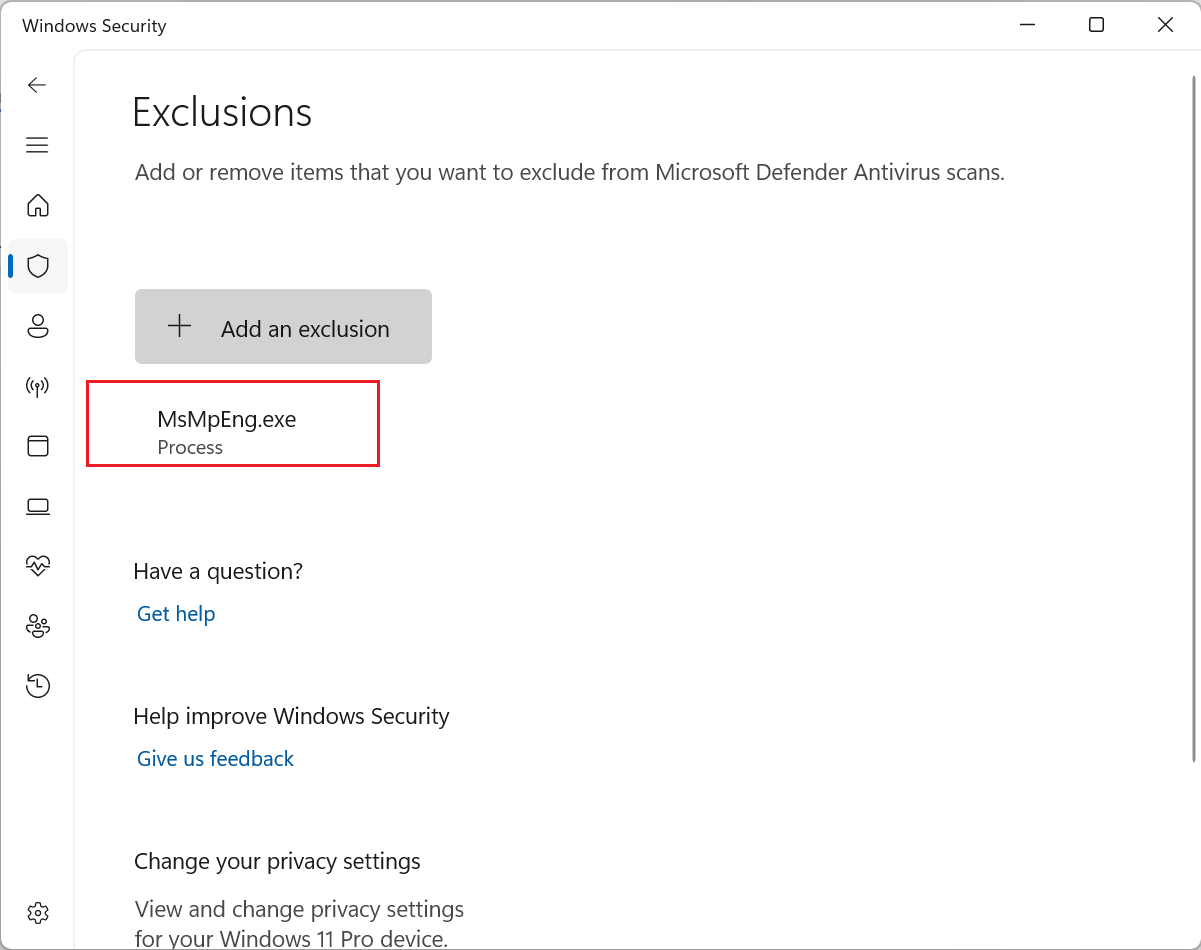
By excluding the Antimalware Service Executable from scans, you can minimize its impact on CPU usage while still maintaining adequate protection against malware.
Conclusion
The Antimalware Service Executable is a critical component of Windows Defender that ensures your system's security. However, its high CPU usage can impact your system's performance. By following the solutions outlined in this article, you can effectively reduce CPU load caused by the Antimalware Service Executable and optimize your system's performance. Remember to perform a clean boot, adjust Windows Defender's schedule, and exclude MsMpEng.exe from scans to minimize its impact on CPU resources.
FAQs
Q1. Why does the Antimalware Service Executable consume a high amount of CPU?
The Antimalware Service Executable consumes a high amount of CPU due to real-time protection, scheduled scans, and excessive file activity. These processes are essential for Windows Defender to protect your system from malware and other security threats.
Q2. Can I disable the Antimalware Service Executable to reduce CPU usage?
Disabling the Antimalware Service Executable is not recommended as it will leave your system vulnerable to malware attacks. Instead, follow the solutions mentioned in this article to optimize its CPU usage without compromising your system's security.
Q3. Will reducing CPU load by the Antimalware Service Executable affect my system's security?
No, reducing CPU load by the Antimalware Service Executable will not affect your system's security. The solutions outlined in this article are designed to optimize CPU usage without compromising the effectiveness of Windows Defender in protecting your system from malware and other threats.
For more such content, visit Medha Cloud
Topics
Bharath Kumar
Senior Microsoft 365 Consultant • 8+ years
Bharath is a Senior Microsoft 365 Consultant specializing in enterprise productivity solutions and white-label IT services. He has successfully deployed Microsoft 365 for over 200 organizations and helps MSPs build scalable white-label partnerships.
